- 多元化社交。 Twitter、Facebook、Google+、微博等社交媒体的发展极大丰富了人们的日常生活。人们在社交媒体中分享观点、聊天、购物等。 如果仅关注一个社交网络(或网络中特定的一种关系)则可能忽略许多有价值的隐含信息,这很可能导致错误的分析结果。
- 跨行交易。 方便快捷的在线支付方式正逐渐取代传统的现金支付和信用卡,同时也为金融犯罪提供了新的方式。如果仅使用图形模型分析来自单个银行的转账记录,其结果可能不完整。 因此,有必要根据所有可能的交易途径收集数据,获取完整信息。
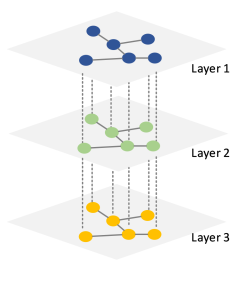
- 城市交通系统。 现代社会的科技进步丰富了人们日常的交通出行方式,例如公交、地铁、电车、磁悬浮等。 在分析公共交通系统时,应充分考虑各种交通方式的特点,特别是对于某些枢纽站应更加重视解决交通拥堵问题。 当公交线路拥塞时,乘客可能选择地铁,这同样会导致地铁的拥挤。 所以本质上,城市交通系统更像是一个多层网络模型(Multilayer network),如图1显示了成都公交地铁网络。

多层网络模型相关研究有2篇比较经典的综述 (Kivelä et al. 2014; Boccaletti et al. 2014). ,里面提及的两个模型本质上很像,但是Kivela 的模型在层内连边和层间连边的基础上进一步考虑了“切面”(aspect)的概念,虽然信息更立体了,但是处理起来也麻烦了一些,如下图2所示。
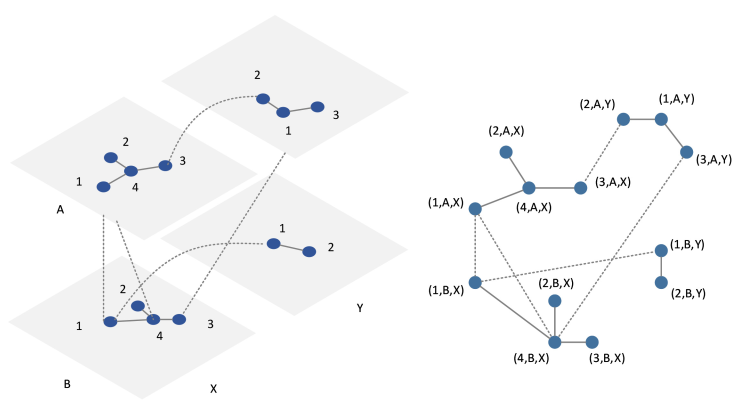
\[\mathcal{M}=\left[\begin{array}{cccc} A_{1} & I_{12} & \cdots & I_{1 L} \\ I_{21} & A_{2} & \cdots & I_{2 L} \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ I_{L 1} & I_{L 2} & \cdots & A_{L} \end{array}\right] \in \mathcal{R}^{N \times N}\]其中,\(A_1,A_2,..., A_L\) 分别表示 \(1, 2,... ,L\) 层的邻接矩阵,\(\mathcal{R}\) 表示实数集合,\(N\) 表示网络中的节点总数,可以通过各层的节点数求和计算,即 \(N=\sum_{1 \leq l \leq L}|V^l|\)。对角线区域的邻接矩阵 \(I_{\alpha\beta}\) 表示各层之间的层间连边,如果用 \(I\) 表示层间连边,那么
\[I=\bigcup_{\alpha,\beta=1,\alpha\neq\beta}^{L}I_{\alpha\beta}\]其中,\(\alpha\) 和 \(\beta\) 表示多层网络中的层(Layer),\(L\) 表示网络的总层数。
常见的社团质量评价指标:
- 模块度(Modularity)[1]:\[Q=\frac{1}{2 m} \sum_{i j}(A_{i j}-\frac{k_i k_j}{2 m}) \delta(C_i, C_j)\]其中,\(m\) 表示网络中的边数,\(k\) 分别表示节点 \(i\) 和节点 \(j\) 的度,\(\delta(C_i,C_j)\) 表示判断节点 \(i\) 和节点 \(j\) 是否在同一社团的克罗内克函数。模块度的取值范围为 [-0.5, 1),通常认为模块度取值在 0.3~ 0.7 之间,划分的社团结构较为明显。
- NMI(Normalized Mutual Information)[2]:
\[\mathrm{NMI}(A,B) = \frac{-2 \sum_{i=1}^{C_A} \sum_{j=1}^{C_B} N_{ij} \log \frac{N_{ij} N}{N_i N_j}}{\sum_{i=1}^{C_A} N_i \log \frac{C_i}{N} + \sum_{j=1}^{C_B} N_j \log \frac{C_j}{N} }\]其中,\(A\) 和 \(B\) 分别表示真实的社团标签以及算法得到的社团发现结果,\(C_A\) 和 \(C_B\) 分别表示 \(A\) 和 \(B\) 的社团个数。\(N_{ij}\) 表示混淆矩阵中的元素,\(N_i\) 和 \(N_j\) 分别表示混淆矩阵中第 \(i\) 行第 \(j\) 列的元素之和。\(N\) 表示网络中节点总数,即混淆矩阵的维度。NMI 的取值范围是 [0,1],如果算法得到的社团划分结果与真实社团标签完全一致,即 \(A=B\), 那么 \(\mathrm{NMI}(A,B)=1\);反之,如果算法得到的社团结果与真实社团标签完全不一致,则 \(\mathrm{NMI}(A,B)=0\)。
多层网络社团划分思路:
- 聚合法:对每层网络分别划分社团,然后进行社团合并。
- 压扁法:将多层网络(多元网络)压扁成加权单层网络,然后利用经典算法进行划分。
- 直接法:直接在多层网络上进行划分。
| Name | Classification | Strategy | Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMM (Tang et al. 2009) | Aggregation | Multilayer modularity maximization | Multi-dimensional |
| MULTICLUS (Papalexakis et al. 2013) | Aggregation | Minimum description length | Multiplex, bipartite |
| GRAPHFUSE (Papalexakis et al. 2013) | Aggregation | Tensor analysis | Multiplex |
| ABACUS (Berlingerio et al. 2013) | Aggregation | Multilayer modularity maximization | Multi-dimensional |
| DNMF (Jiao et al. 2017) | Aggregation | Nonnegative matrix factorization | Multiplex, temporal |
| EMCD (Tagarelli et al. 2017) | Aggregation | Modularity maximization | Multiplex |
| Multilink (Mondragon et al. 2018) | Aggregation | Multilink similarity | Multiplex |
| M-EMCD* (Mandaglio et al. 2018) | Aggregation | Modularity maximization | Multiplex |
| M-Motif (Huang et al. 2019) | Aggregation | Merge partitions across layers | Multilayer |
| MEMM (Zhang et al. 2019) | Aggregation | Multilayer edge mixture model | Multiplex |
| HSBM (Paez et al. 2019) | Aggregation | Hierarchical SBM and Bayes | Multiplex |
| Variational-Bayes (Ali et al. 2019) | Aggregation | SBM and variational Bayes | Multiplex, weighted |
| GenLouvain (Jutla et al. 2011) | Direct | Multiplex map equation | Multiplex, temporal |
| MultiGA (Amelio and Pizzuti 2014b) | Direct | Genetic representation | Multiplex |
| MultiMOGA (Amelio and Pizzuti 2014a) | Direct | Multi-objective optimization | Multiplex |
| CLAN (Dabideen et al. 2014) | Direct | Variational label propagation | Multiplex, temporal |
| LART (Kuncheva and Montana 2015) | Direct | Random walk | Multiplex |
| Multiplex-Infomap (De Domenico et al. 2015a) | Direct | Multiplex map equation | Multiplex |
| LocalNCPs (Jeub et al. 2015) | Direct | Local random walk | Multiplex |
| BAZZI (Bazzi et al. 2016) | Direct | Multilayer modularity maximization | Multiplex, temporal |
| ML-LCD (Interdonato et al. 2017) | Direct | Local objective function maximization | Multiplex |
| GN-QMQM (Pramanik et al. 2017) | Direct | Maximum betweenness edges removal | Multiplex |
| Louvain-QMQM (Pramanik et al. 2017) | Direct | Modularity optimization | Multiplex, weighted |
| MLMaOP (Pizzuti and Socievole 2017) | Direct | Multi-objective Optimization | Multiplex |
| NFC (Aslak et al. 2018) | Direct | Random walk and Infomap | Multiplex, temporal |
| S2-jNMF (Ma et al. 2018) | Direct | Nonnegative matrix factorization | Multiplex |
| MNLPA (Alimadadi et al. 2019) | Direct | Label Propagation | Multiplex, directed, weighted |
| IterModMax (Pamfil et al. 2019) | Direct | SBM and Modularity maximization | Multiplex, temporal |
| TMSCD (Kuncheva and Montana 2017, 2019) | Direct | Spectral graph wavelet | Multiplex, temporal |
| CMNC (Chen et al. 2019) | Direct | Tensor Decomposition | Multiplex |
| MCD-Berlingerio (Berlingerio et al. 2011a) | Flattening | Employing monolayer algorithms | Multi-dimensional |
| CDHIA (Tang et al. 2012b) | Flattening | network integration and k-means | Multi-dimensional |
| AggregationPan (Pan et al. 2018) | Flattening | Cutting edges with weight < threshold | Multiplex, weighted |
| ParticleGao (Gao et al. 2019) | Flattening | Particle Competition | Multiplex, directed, weighted |
常用多层网络可视化工具:
- Muxviz,基于R语言实现,可用于层数较多、大规模网络可视化展示,并可拖动不同角度展示效果。https://www.neusncp.com/user/blog?id=80
- Pymnet,基于Python语言实现,小规模多层网络快速展示。https://www.neusncp.com/user/blog?id=356
- Multinetx,绘制简单的demo效果还可以,可附带超邻接矩阵 https://www.neusncp.com/user/blog?id=82。但超邻接矩阵的效果还是推荐使用这个:https://www.neusncp.com/api/matrix
经典数据集:
- London Multiplex Transport Network:https://www.neusncp.com/api/view_dataset?dataset_id=191
- EUAirTransportation: https://www.neusncp.com/api/view_dataset?dataset_id=186
- mammalia-voles-plj-trapping-60 (田鼠诱捕网络): https://www.neusncp.com/api/view_dataset?dataset_id=183
参考文献:
- Newman ME, Girvan M (2004) Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys Rev E69(2):026113
- Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Duch J, Arenas A (2005) Comparing community structure identification. J StatMech Theory Exp 20055(09):P09008
扩展阅读:
Huang X, Chen D, Ren T, et al. A survey of community detection methods in multilayer networks[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2020: 1-45.
@article{huang2020survey,
title={A survey of community detection methods in multilayer networks},
author={Huang, Xinyu and Chen, Dongming and Ren, Tao and Wang, Dongqi},
journal={Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery},
pages={1--45},
year={2020},
publisher={Springer}
}

